原文地址:http://forums.ni.com/t5/Developer-Center-Resources/Passing-and-Receiving-Pointers-with-C-C-DLLs-from-LabVIEW/ta-p/3522714
http://blog.csdn.net/dreamdonghui/article/details/76343631
C and C++ functions often accept pointers in their function prototypes. A pointer is basically an integer value representing a memory address.
To pass a pointer to a DLL, that is, the memory address of a value to a DLL from LabVIEW, you have to configure the Call Library Function Node to pass the data by reference, rather than by value. You cannot directly pass in the memory address as LabVIEW does not expose the memory allocation of data to programmers.
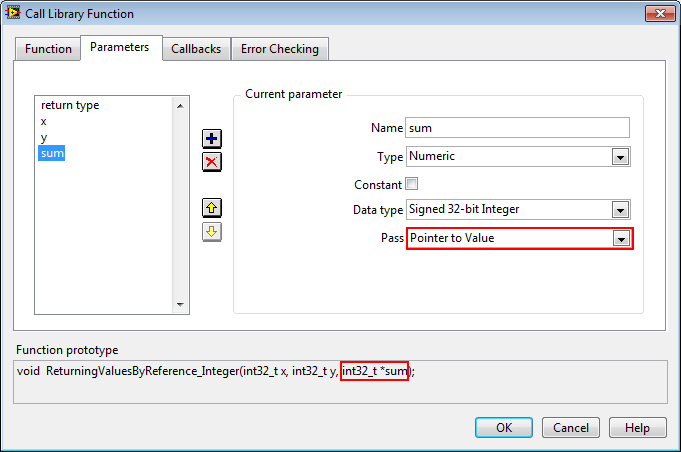
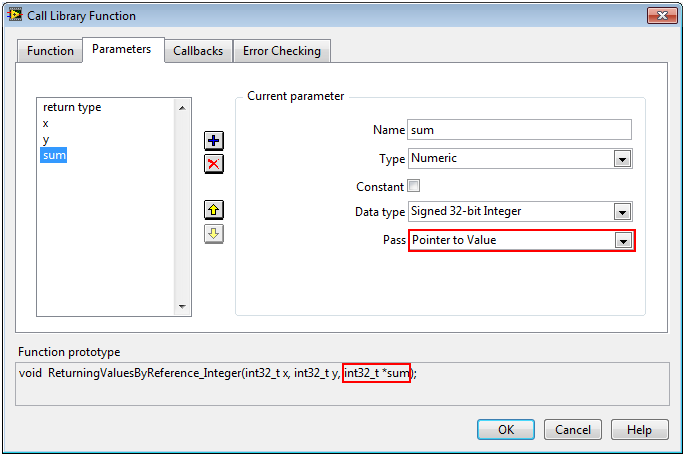
Passing Pointers to Integers (and other primitives)The following is the Call Library Function Node configuration for a function that takes a pointer to an integer. The Pass dropdown should be changed to Pointer to Value.
void ReturningValuesByReference_Integer(int x, int y, int *sum);
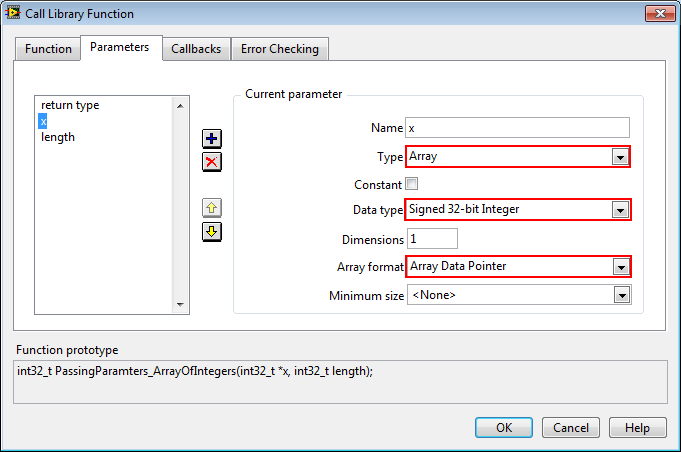
Arrays are by definition pointers in C/C++. This means that an array variable really just holds the memory address of the first element of the array.
The following is the Call Library Function Node configuration for a function that takes an array of integers. The Type should be set to Array. Pick the appropriate data type for the array (integer in this case), and leave the default Array Format dropdown value, Array Data Pointer.
int PassingParamters_ArrayOfIntegers (int x[], int length);
Strings are a special case because a string is really just an array of type char. Because of this, by default, they are already passed by reference.
The following is the Call Library Function Node configuration for a function that takes a string input. Leave the String Format as its default – C String Pointer.
int PassingParamters_String (char *str);

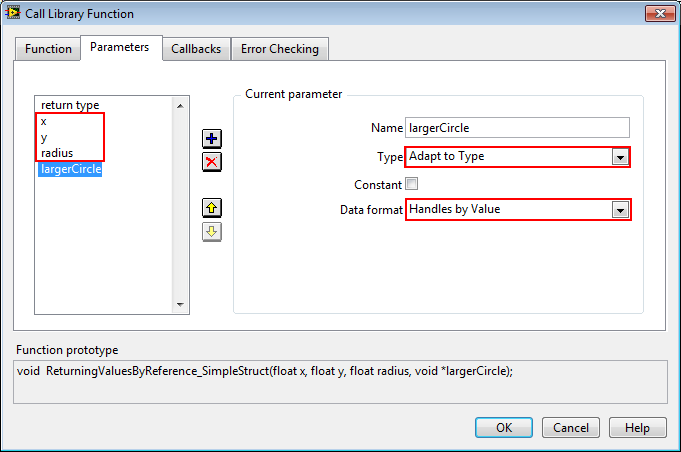
The following is the Call Library Function Node configuration for a function that takes a struct and a pointer to a struct. To pass a struct, you can simply pass in the constituent elements in order, and to pass a pointer to a struct, you can pass the cluster representing the struct as Adapt to Type input with its data format set to Handle by Value.
void ReturningValuesByReference_SimpleStruct (struct simpleStructCircle circle, struct simpleStructCircle *largerCircle);
C/C++ DLLs will often return data using a pointer to the memory location of the value requested. This is done in one of two ways:
1. Returning a pointer: The pointer is returned as the ‘return value’ of the function, as in the following example.
int * ReturnAValue_PointerToInteger(void)
{
int *x = (int *) malloc(sizeof(int));
*x = 5;
return x;
}
Because the Call Library Function Node only allows return types of Integer, String and Void types, you must accept the pointer as an integer representing the memory address and manually dereference the pointer to get its value.
See section Receiving Pointer as Memory Address and Manually Dereferencing
2. Pass by Reference: The pointer is returned through a parameter of the function
void ReturningValuesByReference_Integer (int x, int y, int *sum)
{
//sum is a pointer
*sum = x + y;
}
Based on the data typed returned, you can either automatically dereference the pointer (such as numerics and simple structs), or accept the pointer as an integer value representing the pointer and manually dereference the pointer to get its value.
See section Receiving Pointer as Memory Address and Manually Dereferencing and Receiving Pointer and Automatically Dereferencing
The Call Library Function Node will allow you to automatically dereference pointers to some of the common data types in LabVIEW such as numerics and simple structs. The process to do this is exactly the same as passing a pointer to a DLL, and treating the parameter as an output rather than as in input.
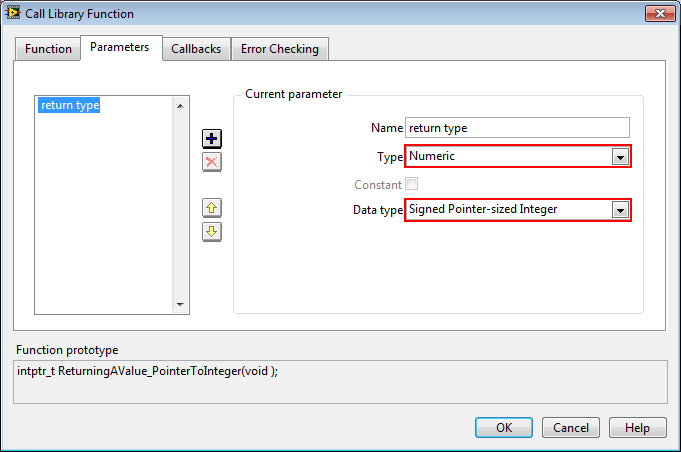
To receive a pointer you must configure the Call Library Function Node to accept an Integer Value. This integer value is the memory address. Once you have the memory address, you must dereference the address to get the actual value.
To configure the Call Library Function Node to receive a pointer, set the Type to Numeric and the data type to Signed Pointer-sized Integer. The Pointer-sized Integer will automatically use the appropriate pointer size (32-bit vs. 64-bit) on the Call Library Function Node based on your OS and LabVIEW.
Note: You will see a coercion dot if you pass a 32-bit Integer to this input, even if you are on a 32-bit OS.
For details on how to dereference the pointer (that is, get the value that the pointer ‘points’ to), refer to:
Dereferencing Pointers from C/C++ DLLs in LabVIEW
For details on how to dereference a pointer in LabVIEW as well as special cases, refer to:
Dereferencing Pointers from C/C++ DLLs in LabVIEW
For examples on handling pointers using both methods described above, refer to:
Calling C/C++ DLLs Containing Simple and Complex Datatypes from LabVIEW
*博客内容为网友个人发布,仅代表博主个人观点,如有侵权请联系工作人员删除。